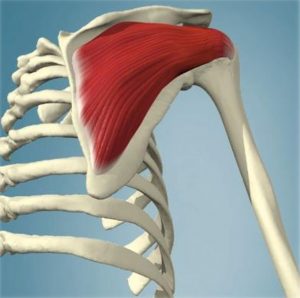
 The infrapinatus muscle is a thick irregular rotator cuff muscle located on the back of your shoulder blade. It has a strong connection to the shoulder and along with teres minor, rotates your arm externally. Most importantly, in conjunction with the other rotator cuff muscles, it is responsible for dynamic stabilization of the shoulder joint, especially during upward movement of your arm.
The infrapinatus muscle is a thick irregular rotator cuff muscle located on the back of your shoulder blade. It has a strong connection to the shoulder and along with teres minor, rotates your arm externally. Most importantly, in conjunction with the other rotator cuff muscles, it is responsible for dynamic stabilization of the shoulder joint, especially during upward movement of your arm.
The shoulder has less connective tissue structure than other major joints. The rotator cuff muscles, including infraspinatus, act as a sort of dynamic muscle/ligament hybrid to stabilize the shoulder joint as you move.
Of the important functions of infraspinatus is to provide force to seat the head of humerus when you extend your arm up.
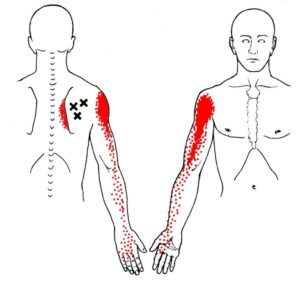
Trigger points in your infraspinatus refer pain deep in the front part of the deltoids, and sometimes extending down the side of your arm past the elbow to the top and thumb side of your forearm and hand. Infraspinatus can also cause pain on the inside edge of your shoulder blade.
Infraspinatus trigger points are often involved with shoulder impingement syndromes and subacromial pain syndrome. Trigger point referrals from infraspinatus can initiate central sensitization leading to chronic shoulder pain.
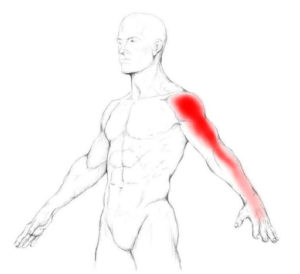 Trigger points in the infraspinatus often cause pain even when you are at rest, as well as interfering with your daily activities and sleep. You may experience a deep ache in the front of your shoulder or deltoids that feels deep in the joint. It can be similar to bursitis.
Pain can spread down your arm past the elbow and to the top and thumb side of your forearm and hand. It can even include the fingers and thumb. This pain can be similar to a C5-C6 cervical issue or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Trigger points in the infraspinatus often cause pain even when you are at rest, as well as interfering with your daily activities and sleep. You may experience a deep ache in the front of your shoulder or deltoids that feels deep in the joint. It can be similar to bursitis.
Pain can spread down your arm past the elbow and to the top and thumb side of your forearm and hand. It can even include the fingers and thumb. This pain can be similar to a C5-C6 cervical issue or carpal tunnel syndrome.
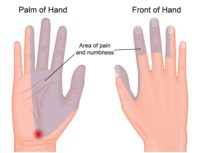 In fact, some studies have found that a third of patients with suspected of carpal tunnel syndrome and EMGs negative for carpal tunnel have infraspinatus trigger points. Others have observed generally that treating infraspinatus trigger points reduces symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
You may also experience significant pain on the inside border of your shoulder blade or pain extending up the side of your neck. Infraspinatus trigger points can contribute to symptoms of mechanical neck pain, post-mastectomy pain, office and industrial workers, or those with a medical diagnosis of subacromial impingement syndrome.
Infraspinatus trigger points contribute to shoulder girdle fatigue, weakness of grip, loss of should mobility and increased underarm sweating. Common compaints include:
In fact, some studies have found that a third of patients with suspected of carpal tunnel syndrome and EMGs negative for carpal tunnel have infraspinatus trigger points. Others have observed generally that treating infraspinatus trigger points reduces symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
You may also experience significant pain on the inside border of your shoulder blade or pain extending up the side of your neck. Infraspinatus trigger points can contribute to symptoms of mechanical neck pain, post-mastectomy pain, office and industrial workers, or those with a medical diagnosis of subacromial impingement syndrome.
Infraspinatus trigger points contribute to shoulder girdle fatigue, weakness of grip, loss of should mobility and increased underarm sweating. Common compaints include:
- I can't reach my back pocket
- I can't fasten my bra behind my back anymore
- I can't reach into the back seat of my car
- I have to put my coat on one sleeve at a time
- I can't play overhead sports
 If your infraspinatus trigger points are on your dominant side you may have difficulty with reaching your head to comb, brush or dry your hair, brush your teeth, apply makeup or shave facial hair. However, if the trigger points are on your non-dominant side, you may not notice even moderate restrictions unless you make movements that are unusual for you.
If you have infraspinatus trigger points you may find that sleeping on the involved side is painful. However, sleeping on the uninvolved side can also cause problems. The pressure of your upper body may cause pressure on the 'good' side and activate trigger points in the infraspinatus on that side. In addition, the upper, painful arm falls forward, causing a prolonged stretch of the infraspinatus, re-activating the originally painful side. Some people find that they need to sleep in a reclined position until their infraspinatus trigger points moderate.
Note that a similar mechanism can occur during surgery. Trigger points in the infraspinatus and other muscles can be activated by sustained pressure or awkward positions during surgery.
Patients who have suffered a stroke and are paralyzed in the shoulder girdle on one side experience significant pain. This is because various muscles develop trigger points on the affected side, including the infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis, trapezius, levator scapula, rhomboids and deltoids. If the muscles are not spastic, they respond well to individual treatment of trigger points.
If your infraspinatus trigger points are on your dominant side you may have difficulty with reaching your head to comb, brush or dry your hair, brush your teeth, apply makeup or shave facial hair. However, if the trigger points are on your non-dominant side, you may not notice even moderate restrictions unless you make movements that are unusual for you.
If you have infraspinatus trigger points you may find that sleeping on the involved side is painful. However, sleeping on the uninvolved side can also cause problems. The pressure of your upper body may cause pressure on the 'good' side and activate trigger points in the infraspinatus on that side. In addition, the upper, painful arm falls forward, causing a prolonged stretch of the infraspinatus, re-activating the originally painful side. Some people find that they need to sleep in a reclined position until their infraspinatus trigger points moderate.
Note that a similar mechanism can occur during surgery. Trigger points in the infraspinatus and other muscles can be activated by sustained pressure or awkward positions during surgery.
Patients who have suffered a stroke and are paralyzed in the shoulder girdle on one side experience significant pain. This is because various muscles develop trigger points on the affected side, including the infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis, trapezius, levator scapula, rhomboids and deltoids. If the muscles are not spastic, they respond well to individual treatment of trigger points.
 When a posture or activity that activates a trigger point is not corrected, it can also perpetuate it. Trigger points can be activated anywhere in the infraspinatus from unaccustomed eccentric loading, eccentric exercise in an unconditioned muscle, maximal or sub-maximal concentric loading.
Placing the muscle in a shortened or lengthened position for an extended period of time can also activate trigger points in the infraspinatus.
Infraspinatus is most often activated by major acute or minor repetitive overload. For instance, frequently reaching to the back seat of a car to tend to an young child is a repeated minor overload.
Losing your balance going down the stairs and suddenly reaching back for the railing is a more significant acute overload. Vigorous weight training with heavy overhead loads is a continued, but acute overload.
Other examples of acute overload include twisting your arm when falling holding a ski pole, a hard tennis serve delivered when slightly off balance or dragging a novice ice skater, luggage or wagon around for a long time. In acute cases, the onset of pain is usually within a few hours of the trauma. You will usually be able to identify the event.
When a posture or activity that activates a trigger point is not corrected, it can also perpetuate it. Trigger points can be activated anywhere in the infraspinatus from unaccustomed eccentric loading, eccentric exercise in an unconditioned muscle, maximal or sub-maximal concentric loading.
Placing the muscle in a shortened or lengthened position for an extended period of time can also activate trigger points in the infraspinatus.
Infraspinatus is most often activated by major acute or minor repetitive overload. For instance, frequently reaching to the back seat of a car to tend to an young child is a repeated minor overload.
Losing your balance going down the stairs and suddenly reaching back for the railing is a more significant acute overload. Vigorous weight training with heavy overhead loads is a continued, but acute overload.
Other examples of acute overload include twisting your arm when falling holding a ski pole, a hard tennis serve delivered when slightly off balance or dragging a novice ice skater, luggage or wagon around for a long time. In acute cases, the onset of pain is usually within a few hours of the trauma. You will usually be able to identify the event.
 Following their first moving vehicle accident, 20% - 30% of individuals developed infraspinatus trigger points, regardless of the direction of impact, a slightly lower rate than the development of supraspinatus trigger points.
In cases of chronic shoulder pain and dysfunction, studies have shown an improvement of 24% in DASH scores (Disability of Arm, Shoulder and Hand) as active trigger points were inactivated. In all there was a 55% improvement pain and function at 12 weeks.
Following their first moving vehicle accident, 20% - 30% of individuals developed infraspinatus trigger points, regardless of the direction of impact, a slightly lower rate than the development of supraspinatus trigger points.
In cases of chronic shoulder pain and dysfunction, studies have shown an improvement of 24% in DASH scores (Disability of Arm, Shoulder and Hand) as active trigger points were inactivated. In all there was a 55% improvement pain and function at 12 weeks.
 Elite swimmers with shoulder pain had significant trigger points in the infraspinatus and subscapularis muscles that reproduced the swimmer's pain. They found active trigger points, inducing referred pain, in the shoulders of swimmers without shoulder pain too. However, when questioned, the swimmers said they recalled having that pain.
Repetitive overuse and overload of the rotator cuff muscles, especially infraspinatus, is also associated with competitive volleyball. Release of those trigger points quickly restored active range of motion and allowed disabled athletes to return to competition.
Elite swimmers with shoulder pain had significant trigger points in the infraspinatus and subscapularis muscles that reproduced the swimmer's pain. They found active trigger points, inducing referred pain, in the shoulders of swimmers without shoulder pain too. However, when questioned, the swimmers said they recalled having that pain.
Repetitive overuse and overload of the rotator cuff muscles, especially infraspinatus, is also associated with competitive volleyball. Release of those trigger points quickly restored active range of motion and allowed disabled athletes to return to competition.
 The infraspinatus muscle can be access easily with a tennis or lacrosse ball. In addition, for more precise location of trigger points you can release infraspinatus yourself using a tool such as the Back Knobber.
The infraspinatus muscle can be access easily with a tennis or lacrosse ball. In addition, for more precise location of trigger points you can release infraspinatus yourself using a tool such as the Back Knobber.
 You may also find that it work well to use this tool laying down. This allows the entire shoulder girdle to relax as you treat the infraspinatus and other muscles.
Maintain pressure for one to two minutes. This self-release can be repeated several times a day until the trigger points are inactivated.
You may also find that it work well to use this tool laying down. This allows the entire shoulder girdle to relax as you treat the infraspinatus and other muscles.
Maintain pressure for one to two minutes. This self-release can be repeated several times a day until the trigger points are inactivated.
 You should also stretch the infraspinatus daily while seated or seated in a warm shower. To stretch all three heads of the muscle, you need to stretch the arm out in front of you first and then behind and up the back.
You should also stretch the infraspinatus daily while seated or seated in a warm shower. To stretch all three heads of the muscle, you need to stretch the arm out in front of you first and then behind and up the back.
 With each exhalation, let the muscle relax and see if you can reach up a little further.
You can deepen this stretch by using reciprocal inhibition to activate the antagonists of the infraspinatus.
Following pressure release or stretching a cold pack may be helpful.
If tightness of the posterior capsule develops it is essential that the connective tissue function with the joint be addressed in addition to restoring normal mechanics of your arm and shoulder while treating trigger points in the infraspinatus.
Treatment will fail and pain relief will be temporary if it is limited to this individual muscle without addressing the mechanics of the entire joint.
With each exhalation, let the muscle relax and see if you can reach up a little further.
You can deepen this stretch by using reciprocal inhibition to activate the antagonists of the infraspinatus.
Following pressure release or stretching a cold pack may be helpful.
If tightness of the posterior capsule develops it is essential that the connective tissue function with the joint be addressed in addition to restoring normal mechanics of your arm and shoulder while treating trigger points in the infraspinatus.
Treatment will fail and pain relief will be temporary if it is limited to this individual muscle without addressing the mechanics of the entire joint.
 Avoid sustained or repetitive actions that overload the infraspinatus muscle such lifting heavy objects overhead, backward or out to the side.
Avoid sustained contraction of the infraspinatus. For example, 20 minutes or more of hairstyling or work overhead can easily activate this muscle. Take short breaks so give the infraspinatus a chance to recover.
Avoid sustained or repetitive actions that overload the infraspinatus muscle such lifting heavy objects overhead, backward or out to the side.
Avoid sustained contraction of the infraspinatus. For example, 20 minutes or more of hairstyling or work overhead can easily activate this muscle. Take short breaks so give the infraspinatus a chance to recover.
 Restful sleep may be difficult due to pain. Consider sleeping on the uninvolved side. If you sleep on the pain-free side your sleep will be improved if you support the painful arm on a pillow, avoiding the prolonged lengthening of infraspinatus that can lead to pain.
Restful sleep may be difficult due to pain. Consider sleeping on the uninvolved side. If you sleep on the pain-free side your sleep will be improved if you support the painful arm on a pillow, avoiding the prolonged lengthening of infraspinatus that can lead to pain.
 You can also use this a variation of this technique to support the painful arm when sleeping on your back or when sitting.
In general, do not sleep on your stomach. Do not lie on either on your back with your arms extended up over your head. This will externally rotate your arms and keep the infraspinatus in a shortened position for an extended time.
You can also use this a variation of this technique to support the painful arm when sleeping on your back or when sitting.
In general, do not sleep on your stomach. Do not lie on either on your back with your arms extended up over your head. This will externally rotate your arms and keep the infraspinatus in a shortened position for an extended time.
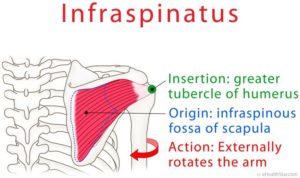 Infraspinatus, along with suprapinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis insert into the lesser and greater tuberosities on the front and back of your humerus. They form a 'cuff' of connnective tissue and muscles around the head of your humerus that help rotate your arm at the shoulder. Collectively, they are called the rotator cuff.
The infraspinatus muscle is the most powerful rotator cuff muscle and is involved in both raising your arm to the side and maintaining stability in your shoulder joint as you do. It also externally rotates your shoulder, as you would when cocking back before a throw.
Infraspinatus, along with suprapinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis insert into the lesser and greater tuberosities on the front and back of your humerus. They form a 'cuff' of connnective tissue and muscles around the head of your humerus that help rotate your arm at the shoulder. Collectively, they are called the rotator cuff.
The infraspinatus muscle is the most powerful rotator cuff muscle and is involved in both raising your arm to the side and maintaining stability in your shoulder joint as you do. It also externally rotates your shoulder, as you would when cocking back before a throw.
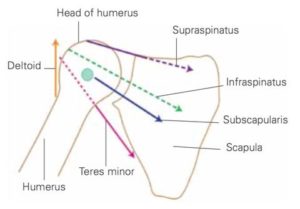 Although each of these rotator cuff muscles participate in the rotation of your arm, their primary purpose is to pull the head of humerus fairly tight into the shallow socket of the shoulder blade. Unlike your knee or ankle, this stability is created by largely these rotator cuff muscles, not ligaments. It part of what allows us to have much greater range of motion at our shoulder than any other joint. For this stabilizing function, you could think of them as powered, dynamic ligaments.
Infraspinatus passively prevents dislocation towards the rear of the shoulder and actively prevents dislocation towards the front through the rotator cable.
As the strongest posterior rotator cuff muscle, infraspinatus is also a powerful external rotator of your arm. External rotation is necessary for full elevation of your arm at the shoulder joint. However, movement at the shoulder joint is a complex, coordinated activity. However, infraspinatus is most effective in external rotation with the arm lowered from 0 to 10 degrees of abduction.
Although each of these rotator cuff muscles participate in the rotation of your arm, their primary purpose is to pull the head of humerus fairly tight into the shallow socket of the shoulder blade. Unlike your knee or ankle, this stability is created by largely these rotator cuff muscles, not ligaments. It part of what allows us to have much greater range of motion at our shoulder than any other joint. For this stabilizing function, you could think of them as powered, dynamic ligaments.
Infraspinatus passively prevents dislocation towards the rear of the shoulder and actively prevents dislocation towards the front through the rotator cable.
As the strongest posterior rotator cuff muscle, infraspinatus is also a powerful external rotator of your arm. External rotation is necessary for full elevation of your arm at the shoulder joint. However, movement at the shoulder joint is a complex, coordinated activity. However, infraspinatus is most effective in external rotation with the arm lowered from 0 to 10 degrees of abduction.
 For instance, when your middle deltoid abducts and elevates your shoulder, the head of your humerus wants rise up out of the socket. The lever arms of the rotator cuff generally exert their force down and in towards the joint. In conjunction with your subscapularis, infraspinatus resists this upward force and keeps the humerus down in the socket. In fact, some studies have shown that ALL the rotator cuff muscles activate just before the arm raises in abduction.
Infraspinatus is active linearly as load increases with abduction of your arm. There are also peaks of activity during flexion of your shoulder. The other muscles activate more strongly later in the movement. Individually, the certain rotator muscles are recruited early and different muscles activate later, keeping the head of the humerus stable in most movements.
For instance, when your middle deltoid abducts and elevates your shoulder, the head of your humerus wants rise up out of the socket. The lever arms of the rotator cuff generally exert their force down and in towards the joint. In conjunction with your subscapularis, infraspinatus resists this upward force and keeps the humerus down in the socket. In fact, some studies have shown that ALL the rotator cuff muscles activate just before the arm raises in abduction.
Infraspinatus is active linearly as load increases with abduction of your arm. There are also peaks of activity during flexion of your shoulder. The other muscles activate more strongly later in the movement. Individually, the certain rotator muscles are recruited early and different muscles activate later, keeping the head of the humerus stable in most movements.
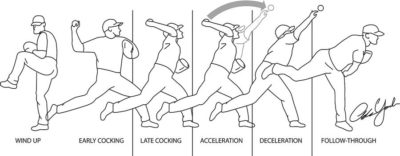 During a throwing motion, infraspinatus is a primary decelerator of your arm. This deceleration requires strong eccentric, lengthening contractions. This can cause the development of trigger points in the infraspinatus. It may also contribute to the breakdown of the undersurface of the infraspinatus tendon.
When you throw, there is a strong force separating the head of the humerus from the socket of the shoulder. This force is resisted by a strong eccentric contraction of infraspinatus. This can lead to overload.
The structure of the shoulder joint and actions of several muscles coordinate to prevent the head of the humerus from moving down, even under significant load or when you are tired. However, in other positions, we don't have this protection and additional contraction of the rotator cuff muscles, including infraspinatus, is necessary.
In golf, activity in the infraspinatus is most active in decelerating your swing during follow through.
When driving, infraspinatus activates most strong when returning the wheel to center after a turn. It also activates when making a turn. When driving straight, shoulder muscle co-contract to center the wheel.
During a throwing motion, infraspinatus is a primary decelerator of your arm. This deceleration requires strong eccentric, lengthening contractions. This can cause the development of trigger points in the infraspinatus. It may also contribute to the breakdown of the undersurface of the infraspinatus tendon.
When you throw, there is a strong force separating the head of the humerus from the socket of the shoulder. This force is resisted by a strong eccentric contraction of infraspinatus. This can lead to overload.
The structure of the shoulder joint and actions of several muscles coordinate to prevent the head of the humerus from moving down, even under significant load or when you are tired. However, in other positions, we don't have this protection and additional contraction of the rotator cuff muscles, including infraspinatus, is necessary.
In golf, activity in the infraspinatus is most active in decelerating your swing during follow through.
When driving, infraspinatus activates most strong when returning the wheel to center after a turn. It also activates when making a turn. When driving straight, shoulder muscle co-contract to center the wheel.
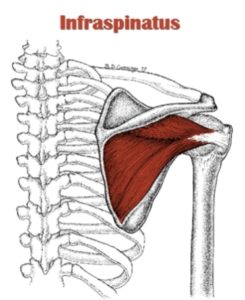 The infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint.
The infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint.
Structure
It is contained within the infraspinatus fascia. This is a tough sheet of connective tissue that lines the depression on the back of your scapula and completely envelops the muscle and separates it from the teres major and teres minor. Muscle fibers arise out of this depression is the shoulder blade and from the fascia itself. It originates from the inside 2/3 of this 'fossa' in the scapula and the fascia of the lower trapezius, rhomboids and serratus anterior. It progresses towards your shoulder where it develops a fascial connection with your rear deltoid.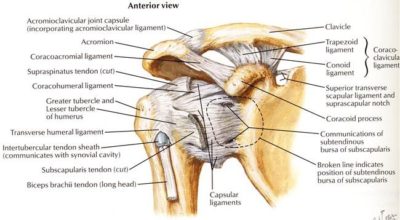 Finally its tendon inserts laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. Some fibers may blend into the top and rear of the joint capsule. This infraspinatus tendon actually begins to fuse with the supraspinatus tendon just as passes the outside edge of the shoulder blade.
There are three sections, or partitions, of infraspinatus; superior (top), middle and inferior (bottom). Like its partner subscapularis, the fibers of the top section run horizontally (transverse), but the middle and lower fibers are angled up towards the shoulder joint and converge into a central thickened tendon.
The cranial (transverse) band– This is the upper horizontal part that originates from below spine of the scapula, and progresses towards the shoulder to attach to the angled area at the middle portion of the tendinous part. The tendinous portion of the transverse band is made up of thin membrane-like tissue, which attaches to the tendinous portion of the angled area – but does not reach the greater tuberosity. Some researchers suggest that this upper part shares innervation with the supraspinatus, making these fibers more like the supraspinatus than infraspinatus.
Finally its tendon inserts laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. Some fibers may blend into the top and rear of the joint capsule. This infraspinatus tendon actually begins to fuse with the supraspinatus tendon just as passes the outside edge of the shoulder blade.
There are three sections, or partitions, of infraspinatus; superior (top), middle and inferior (bottom). Like its partner subscapularis, the fibers of the top section run horizontally (transverse), but the middle and lower fibers are angled up towards the shoulder joint and converge into a central thickened tendon.
The cranial (transverse) band– This is the upper horizontal part that originates from below spine of the scapula, and progresses towards the shoulder to attach to the angled area at the middle portion of the tendinous part. The tendinous portion of the transverse band is made up of thin membrane-like tissue, which attaches to the tendinous portion of the angled area – but does not reach the greater tuberosity. Some researchers suggest that this upper part shares innervation with the supraspinatus, making these fibers more like the supraspinatus than infraspinatus.
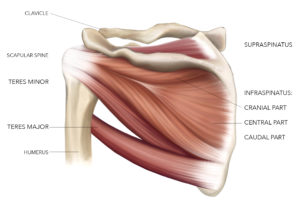 The central (oblique) band– The diagonal part is a fan-shaped muscle bundle, which originates from the depression of the scapula and runs at an upward angle towards the shoulder joint. The diagonal and horizontal parts fuse together at the upper margin. The diagonal part occupies most of the muscular and tendinous portion of the entire infraspinatus. The distinct features of the diagonal part are:
The central (oblique) band– The diagonal part is a fan-shaped muscle bundle, which originates from the depression of the scapula and runs at an upward angle towards the shoulder joint. The diagonal and horizontal parts fuse together at the upper margin. The diagonal part occupies most of the muscular and tendinous portion of the entire infraspinatus. The distinct features of the diagonal part are:
- Almost the entire tendinous portion of the muscle is derived from the oblique (diagonal) part of the infraspinatus.
- The tendinous portion of the oblique part becomes longer and thicker towards the top.
- The uppermost part of the tendinous portion of the the diagonal part reaches the most forward edge of the greater tuberosity.
Relations
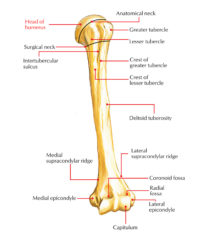 The middle partition of infraspinatus has distinct fibrous band inserting deep to the upper and lower partitions. It appears to attach to the middle and superior facet of the greater tubercle along along with supraspinatus. These deeper fibers pass at sharp angles to merge with the supraspinatus muscle above and cross the rotator cuff interval, finally attaching to the biceps tendon and subscapularis tendon on the front of the shoulder. The combined structure is thick fibrous tendon is called the rotator cable, linking the front and back sides of the rotator cuff together.
The middle partition of infraspinatus has distinct fibrous band inserting deep to the upper and lower partitions. It appears to attach to the middle and superior facet of the greater tubercle along along with supraspinatus. These deeper fibers pass at sharp angles to merge with the supraspinatus muscle above and cross the rotator cuff interval, finally attaching to the biceps tendon and subscapularis tendon on the front of the shoulder. The combined structure is thick fibrous tendon is called the rotator cable, linking the front and back sides of the rotator cuff together.
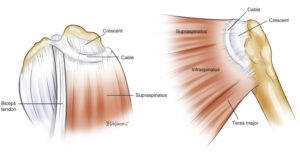 The rotator crescent is the terminal connection of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons that inserts onto the humerus next to the rotator cable. The rotator cable protects the rotator crescent by intrinsically transferring forces from the upper rear side of the rotator cuff to the front.
The rotator crescent is the terminal connection of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons that inserts onto the humerus next to the rotator cable. The rotator cable protects the rotator crescent by intrinsically transferring forces from the upper rear side of the rotator cuff to the front. 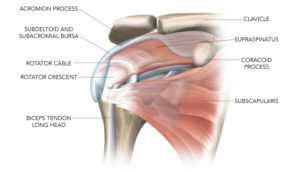 This complicated arrangement allows the rotator cuff to work in a coordinated way no matter how your shoulder moves.
The trapezoidal insertion of the infraspinatus onto the humerus is much larger than the equivalent insertion of the supraspinatus, one reason why the stronger infraspinatus is involved in rotator cuff tears almost as frequently as the supraspinatus.
This complicated arrangement allows the rotator cuff to work in a coordinated way no matter how your shoulder moves.
The trapezoidal insertion of the infraspinatus onto the humerus is much larger than the equivalent insertion of the supraspinatus, one reason why the stronger infraspinatus is involved in rotator cuff tears almost as frequently as the supraspinatus.
