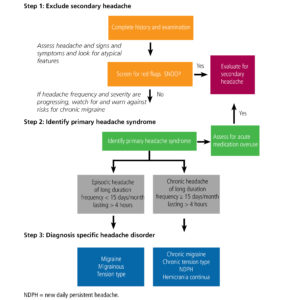
Migraine headache – myofascial therapists see the entire range! With any given occurence, a true migraine sufferer is devastated. Over time, chronic migraines can destroy their lives.
If you have headaches that are especially severe or are on one side of your head, you probably refer to it as a migraine headache – myofascial therapy can probably help! For more information on headaches in general, please see this intro.
You may have had some other types of headaches that are similar so it can be confusing.
In fact, doctors have changed their definitions of migraine headache over the years too. So don’t feel bad if you aren’t sure!
For our purposes, migraines are throbbing, severe headaches. They may be on both sides or one side of your head.1. They have a sick quality that is much like a bad hangover. Generally, it is not responsive to OTC medication
However, if you have bad chronic tension headaches, they might feel very much like migraines. The biggest difference is that your ‘migraines’ probably also have ‘aura‘.
Also, migraines have ‘triggers’. These events, substances, behaviors and other things in our environment seem to set off our migraine attacks2.
Unfortunately, traditional treatment, including primarily drug therapy, has limited success. For treatment of migraine headache pain – myofascial factors can be a powerful tool for relief.
Migraine Headache Characteristics

The pain of your migraine often starts on one side, often behind or around your eye or temple. It is usually on the same side. It can also be on both sides.
Most days, it seems like it comes on gradually for you. Then, as it becomes more severe, you experience a throbbing feeling and physical activity makes it worse. You used to get an “aura” before it started, but that doesn’t happen all the time anymore. Something seems to ‘trigger‘ your headaches. Lately, you’ve been making a list.
Your sister gets migraines too, but hers are on both sides and seems to involve her neck more than yours. However, she doesn’t get the aura that you do. But you don’t get the pain in the back of your head and on the top that she gets.
Unfortunately, your nephew gets them too, but they only last an hour or two.
Other Migraine Symptoms
Even worse, all three of you get nauseated during your migraines. In fact, you and your nephew even vomit sometimes. Bright light and loud sounds are a problem for both you and your sister.
Sometimes, you also have blurred vision, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, frequent urination, or sweating.
Well, no wonder you just prefer to go to your bedroom, close the door and draw the curtains!
The pain of your migraine will typically last 4 to 72 hours in adults. However in young children, it often lasts less than 1 hour.
The frequency of your attacks can vary from a few in a lifetime to several a week.
In our experience, migraine attacks are likely to last multiple days and occur several times a month.
Medications are more effective if used earlier in an attack. The frequent use of medications may result in medication overuse headache, in which the headaches become more severe and more frequent. This may occur with triptans, ergotamines, and analgesics, especially opioid analgesics. Due to these concerns simple analgesics are recommended to be used less than three days per week at most.
Analgesics
Recommended initial treatment for those with mild to moderate symptoms are simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or the combination of acetaminophen, aspirin, and caffeine. Several NSAIDs, including diclofenac and ibuprofen have evidence to support their use. Aspirin can relieve moderate to severe migraine pain, with an effectiveness similar to sumatriptan. Ketorolac is available in an intravenous formulation.
Triptans
Triptans such as sumatriptan are effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people. When sumatriptan is taken with naproxen it works better. They are the initially recommended treatments for those with moderate to severe pain or those with milder symptoms who do not respond to simple analgesics. The different forms available include oral, injectable, nasal spray, and oral dissolving tablets. In general, all the triptans appear equally effective, with similar side effects. However, individuals may respond better to specific ones. They are not addictive, but may cause medication-overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.
Ergotamines
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms. They appear equally effective to the triptans and experience adverse effects that typically are benign. In the most severe cases, such as those with status migrainosus, they appear to be the most effective treatment option. They can cause vasospasm including coronary vasospasm and are contraindicated in people with coronary artery disease.
Other
Intravenous metoclopramide, intravenous prochlorperazine, or intranasal lidocaine are other potential options. Metoclopramide or prochlorperazine are the recommended treatment for those who present to the emergency department. Haloperidol may also be useful in this group. A single dose of intravenous dexamethasone, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours. It is recommended that opioids and barbiturates not be used due to questionable efficacy, addictive potential, and the risk of rebound headache.
Topiramate and botulinum toxin (Botox) have evidence in treating chronic migraine. Botulinum toxin has been found to be useful in those with chronic migraines but not those with episodic ones. The anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody erenumab was found in one study to decrease chronic migraines by 2.4 days more than placebo.
Migraine Headache – Myofascial Therapy

Chronic Headache - Myofascial TriggerPoint Referral Patterns
We can clearly see how referral patterns of head and neck muscles evoke the pain patterns of migraines, tension headaches, cervicogenic headaches. They even overlay the symptoms of cluster headaches and TMJ headache pain. Some of the factors that activate those muscles may not covered by doctors. Those activation factors are things we care a lot about.Myofascial activations are a part of most headache patterns!
Repetitive Use
When ever we are making repetitive movements, we should be mind of using proper body mechanics. This will help minimize repetitive stress injuries and myofascial activations. For instance, lifting in a stooped posture and then twisting is always ill-advised. Doing it repetitively is worse. Therefore, if this type of lifting is required, we should rethink the task and try to organize it in a way that reduces stooping and twisting. However, even simple movements matter. For instance, what if your desk is arranged phone on the wrong side. In fact, with every call, you have to twist your head and neck and reach over with your arm to the wrong side of the desk This is poor body mechanics. Fixing it might be as simple as moving the phone. It pays to think about basic body mechanics in this common sense way each time we engage in a repetitive activity. Fortunately, we're starting to teach this important skill to young people, as in this student guide at University of Michigan.Overload
We can experience chronic overload when we do things like wear high heels, carry a heavy bag or lean into our work. However, acute overload happens when we decide to lift, push, pull or otherwise move something that is too heavy for us. Most often, we overload our muacles with an eccentric contraction. For example, lifting a heavy box, correctly using your legs instead of your back, requires concentric contractions of your quads. However, setting that same heavy box down, slowly and with control, require eccentric, lengthening contractions. These should be done carefully.Spill it!
Of course, if you have a diagnosis from your doctor, we need to know. If you have recent imaging or other test results, even better! We've all been knocked around a bit. We'd like to know everything you can think of about prior accidents, injuries, surgeries and other treatments. It is important to know about previous or current medical conditions that could impact our treatment. Anything from high blood pressure to TMJD to disc problems are vital information. Hopefully, medications align with your diagnosis. Sometimes, certain medications will also modify our reatment options. Some drugs interfere with nutrient absorbtion. Increasingly, supplement use is common and we'll review that with you as well.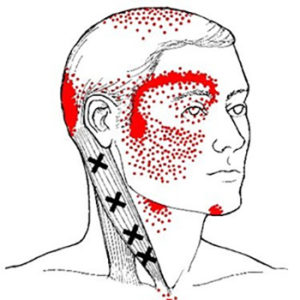
Migraine Headache – Myofascial Referrals Overlap
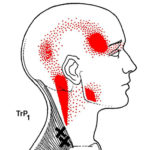 Surprisingly, There are several common patterns that are similar to the pain patterns of migraine headaches. For example, the patterns of the SCM, upper trapezius and temporalis muscles all refer pain strongly to the side of the head and the area above and behind the eyes.
Surprisingly, There are several common patterns that are similar to the pain patterns of migraine headaches. For example, the patterns of the SCM, upper trapezius and temporalis muscles all refer pain strongly to the side of the head and the area above and behind the eyes.
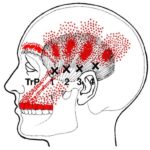 In addition, trigger points in some of these muscles can also cause nausea, blurred vision, vertigo, sensitivity to light and other hearing and visual disturbances. Sound familiar?
In addition, trigger points in some of these muscles can also cause nausea, blurred vision, vertigo, sensitivity to light and other hearing and visual disturbances. Sound familiar?
Where Exactly Is Your Pain?
First, take a moment to consider where your own pain is during a migraine attack. We will usually have you draw it. Pay more attention to the location and how it radiates than how good your art skills are. Of course, knowing the location accurately is more important.
Where Does The Pain Refer?
Next, we take a look at referral patterns for that part of the body.
Sometimes, there is more than one referral pattern that seems to match your pain.
Myofascial referrals may explain most of your pain pattern!

Trigger Point Therapy can get at some aspects of myofascial pain that you might not have thought of!

Myofascial tigger point therapy - it's how you work this!
Manual Therapy Techniques
First, we specifically expertly use manual pressure release therapy, neuromuscular techniques, and deep stroking, friction, skin rolling. When indicated, we also use fascial stretching. Sometimes, we use less common techniques like cupping, spray and stretch and acoustic compression.Muscle Activation
In addition, we may also use active and passive muscle activation techniques. This includes reciprocal inhibition, postisometric relaxation, contract/relax, strain/counter-strain and muscle energy techniques. Sometimes, we also use hot/cold therapy.Range of Motion/Testing
Finally, routinely run the muscle we are treating through its entire, pain-free range of motion. This is part of your treatment. However, it also the start of a new test/assess cycle. We learn together whether your range of motion has increased and whether your pain is reduced. We may have you get up and use your body in the way that causes pain to 'test' more dynamically. As we finish our hand-on work, we transition into learning new movement strategies and self-care.Myofascial tigger point therapy - it's how you work this!
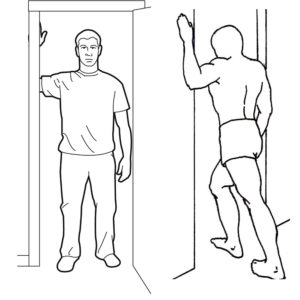
First of all, vigorous stretching of your neck can cause problems. At first, we only engage in limited, gentle stretching of the neck.
Migraines and Blood Flow
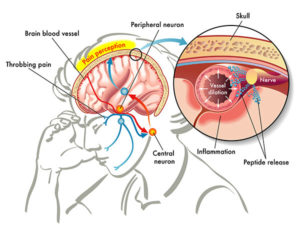
Besides, part of the idea is that the pain of migraine is caused by swelling and inflammation of blood vessels in your brain. Reducing the blood pressure within the brain seems like a good idea. This can happen by either reducing the flow and pressure to the brain (as in biofeedback, for instance) or improving venous drainage from your head.
Myofascial treatment can get at some root causes of migraine than you might not have thought of!
For instance, your pec minor can restrict blood flow to your arm. Releasing this muscle, stretching it and facilitating better blood flow to your arm can reduce incidence and pain of migraines. Our article on Opening The Chest might be helpful.
In addition, we can also treat the subclavius muscle to improve venous drainage. This small muscle runs between the lower edge of your collarbone and rib cage. Taut bands can restrict the veins that drain blood from your head.
In myofascial treatment, we usually passively run the muscles we’re working on through their full pain free range of motion. So, that means that you don’t use the muscle to move it. Either someone does it for you or you use props to minimize active use of the muscle. However, we don’t just gently stretch it. Importantly this means we also shorten the muscle
Myofascial treatment can get at some root causes of migraine than you might not have thought of!

What we do for ourselves during an attack is quite different from what we may do in between attacks. You will want to approach any type of treatment cautiously during an attack. When you have recovered from the attack, more engaged self-care approaches work better.
Frankly, you are not going to feel like stretching or other exercise during a migraine attack. If you could muster the motivation and energy, it would probably make you feel worse anyway.
Therefore, we recommend avoiding stretching and strength training during this time. Instead, focus on self-compression of key muscles in the head and neck that you have worked on with your therapist.
Awesome tools like the Backknobber can be used lying down during an attack. This way, there are no worries about vertigo or nausea and you can completely relax.
The leverage of the tool and pinning it between your body and floor allows access to quite a number of posterior neck muscles. This approach can also be used with some large chairs, recliners and couches when sitting.
There are other approaches to passive self-compression for muscles of the head.
This is the time for well needed stretches of your pecs, SCM, upper traps and levator scapula. It is the time to explore problems with the muscles of your TMJ more thoroughly. In addition, this is the time to strengthen your deep cervical flexors, serratus anterior, lower traps and other postural muscles.
Myofascial self-care can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines!
Specific Causes of Migraine Headache
Some Migraine Headache Causes
Some of the research has suggested that the answer could be, “Yes”.
In fact, we know that migraines are often aggravated by things that increase blood flow to the brain. For instance, exercise or ED medications. In addition, they are often relieved by activities that draw blood flow away from the brain. For instance, biofeedback training3.
Studies About Blood Flow and Migraines
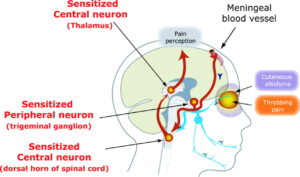
There have been many studies regarding blood flow to the brain and migraines. The idea is that the pain is caused by dilation/swelling and inflammation of blood vessels in your brain4.
Some support this role of peripheral activation. For example, via the sensory nerves that surround blood vessels of your head and neck. In particular, the role of vasodilatation of the arteries in your scalp may be significant.
Treating Vascular Migraine Symptoms
Therefore, the idea in some forms of treatment is to reduce local blood pressure within the brain. For example, this can happen by reducing the flow and pressure to the brain. For instance, we could reduce high blood pressure. Instead, we could also reduce the size of swollen arteries or relax swollen veins. Your doctor might prescribe certain drugs that target key blood vessels.
This is also how some forms of biofeedback work. They “steal” some of the blood otherwise destined for the brain and direct it to your arm.
Myofascial Approaches
Of course, there are other drug-free ways to approach this issue. For instance, in some people, the pec minor is restricting blood flow to the arm. Therefore, releasing this can have an effect similar to biofeedback.
In addition, the taut bands in the subclavius muscle can restrict venous drainage from the head. Releasing this muscle has been shown to help relieve migraines. Another technique is open the adductor hiatus, near the groin, permitting greater blood flow to the legs.
Allodynia
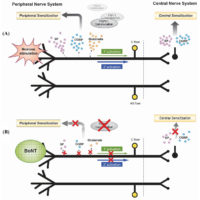
Allodynia occurs when you experience pain from things that are normally not painful. For example, simple touch or pressure become painful. Nerves in the area that was touched sends signals to your brain. But, your nervous system is in a heightened state. So, your brain doesn't produce a mild sensation of touch as it should. Instead, it produces a sensation of pain and discomfort.Hyperalgesia
Hyperalgesia occurs when something that typically painful is more painful than it should be. For example, a simple bump would ordinarily be mildly painful. However, if you are a chronic pain patient it might send your through the roof. Again, your nervous system is more sensitive. Of course, it produces pain that is amplified.Other Symptoms of Central Sensitization
Central sensitivity has other characteristics. They occur less often. For example, it can lead to heightened sensitivities across all your senses. For instance, some chronic pain patients report sensitivities to light, sounds and odors. Normal levels of light can seem too bright. Perfume can produce a headache... In addition, central sensitivity is associated with cognitive deficits. For instance, this includes poor concentration and poor short-term memory. Also, it corresponds with increased levels of emotional distress, particularly anxiety. After all, the nervous system isn't just responsible for sensations, like pain. In addition, it produces our emotions. Central sensitivity can occur with chronic low back pain, chronic neck pain, whiplash injuries, headaches and other conditions.Fortunately, for Chronic Pain - Myofascial Trigger Point Therapy helps break the cycle of central sensitivity...
Local Causes
Chronic pain begins with a peripheral or local issue of some type. For instance, it could be an injury, a surgery or a myofascial trigger point. Or, in some types of chronic headaches, the local cause can include pain from swelling blood vessels. Instead, in a low back injury, it could be compression of a nerve root. In fact, the initial pain of the peripheral stimulus can vary greatly. However, if the pain is severe/and or recurs, our perception of it can change.Transition to Chronic Pain
Eventually, the recurring local pain response is transformed into a centralized pain response. Over time, these changes in peripheral pain pathways increase the excitability of the central nervous system pain pathways. This increased sensitivity makes another pain episode more likely and more severe. Ultimately, this results in the transition of your episodic pain into chronic pain. More precisely, hyperexcitability occurs in the trigeminal spinal nucleus, thalamus, and cerebral cortex. This causes central sensitization. We experience this as the allodynia and pain of chronic headache, low back pain and more.Fortunately, is you have chronic pain – myofascial trigger point therapy works!
Other Migraine Facts
Causes of Aura and Migraine
Cortical spreading depression (CSP) is a burst of neuronal activity followed by a period of inactivity. We see CSP in those with migraines with an aura. There are a number of explanations for this. This includes activation of NMDA receptors leading to calcium entering the cell.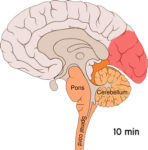 Next, after the burst of activity, the blood flow to the cerebral cortex area decreases for two to six hours.
Next, after the burst of activity, the blood flow to the cerebral cortex area decreases for two to six hours.
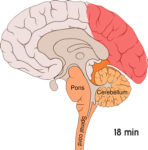 Finally, depolarization travels down the underside of the brain. Then, nerves that sense pain in the head and neck are triggered and we feel migraine headache pain. The animation of this process is interesting.
Another important theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex. This combines with abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem. In addition, low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin may be involved.
Clearly, this is one of the reasons that anti-depressants are sometimes used in the treatment of migraines.
Finally, depolarization travels down the underside of the brain. Then, nerves that sense pain in the head and neck are triggered and we feel migraine headache pain. The animation of this process is interesting.
Another important theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex. This combines with abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem. In addition, low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin may be involved.
Clearly, this is one of the reasons that anti-depressants are sometimes used in the treatment of migraines.
 This could be dilated blood vessels, trigger points in muscles, etc. Next, this kicks off a neurological process where we become more sensitive to pain. This creates a forward feedback loop that make you miserable until the cycle breaks.
This could be dilated blood vessels, trigger points in muscles, etc. Next, this kicks off a neurological process where we become more sensitive to pain. This creates a forward feedback loop that make you miserable until the cycle breaks.
What is the difference between a chronic tension headache and a migraine?
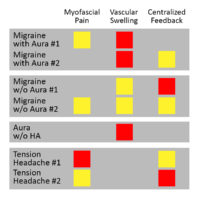
In both types of headaches, they become chronic when central sensitization happens. However, the variations and significance of migraine aura are only starting to be appreciated. In 1991, Oleson focused on three key aspects of chronic headaches. First, the "peripheral" stimulus of myofascial pain. This includes the pain of swelling blood vessels and the central sensitivity of the nervous system itself. Essentially, he showed that mild or moderate myofascial pain is reinforced by central nervous system sensitization. This was true in both migraines and tension headaches. In addition, he showed that even a mild combination of vascular swelling plus myofascial pain OR central sensitization causes migraines. Finally, there was aura when the swelling was severe. However, sometimes, the primary symptom is aura with no headache. Then, patients have swelling of the blood vessels WITHOUT myofascial pain or central reinforcement.The involvement of blood vessels in your scalp is really what makes a migraine...
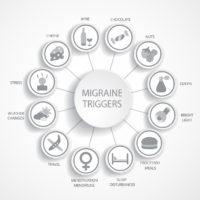
- Certain foods - For example, aged cheeses and salty and processed foods might trigger migraines. Also, skipping meals or fasting.
- Some additives - These include the sweetener aspartame and the preservative monosodium glutamate (MSG), found in many foods.
- Odors and chemicals - Strong smells including perfume, paint thinner, secondhand smoke and others, trigger migraines in some people.
- Bright lights, sounds - Bright lights and sun glare can induce migraines. Also, loud sounds.
- Changes in weather - For instance, a change of weather or barometric pressure can prompt a migraine.
- Hormone levels - Fluctuations in estrogen levels seem to trigger headaches in many women.
- Physical activity - Intense physical exertion, including sexual activity, might provoke migraines.
- Some medications - Oral contraceptives and vasodilators, such as nitroglycerin, can trigger migraines.
Migraine Headache Phases

Prodromal symptoms can warn you of oncoming migraines. In fact, these occur in about two thirds of people. However, the length of time until the Aura/Pain phases varies greatly. It can range from two hours to two days.
Your symptoms during this warning phase can include a wide variety of phenomena. This includes altered mood, irritability, depression or euphoria and fatigue. Other symptoms include craving for certain food(s), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), constipation or diarrhea, and sensitivity to smells or noise.
Well, this sounds like a lot what might happen to most of us feel on a stressful day when we aren’t coping well. So, is this really a “prodrome” of a migraine? Maybe, but it could also be the beginnings of a tension headache or an inflammatory digestive episode.
Of course, there are days when we manage this stress more effectively. On other days it gets the better of us. Neuroimaging studies show us the limbic system and hypothalamus are origin of prodromal symptoms in migraine. Interestingly, these areas in the brain are deeply connected to both emotional and physical balance.
Prodrome can occur whether you have migraine with aura or migraine without aura.
Fortunately, during the prodrome of migraine headache – myofascial self-care and therapy approaches can lessen or avoid an attack.
After the early warning signs of prodrome, but before the pain phase starts, you may experience auras of various types.
Usually, auras appear gradually over a number of minutes and last less than a hour. We tend to think of this as a visual experience. However, aura symptoms can be visual, sensory or motor in nature. Also, you could experience more than one. Learn more about the causes of migraine aura.
Visual Aura
Vision disturbances often consist of a scintillating scotoma. This an area of partial alteration in your field of vision which flickers and may interfere with your ability to read or drive.
Typically, these start near the center of your vision and then spread out to the sides with zigzagging lines. These have been described as looking like fortifications or walls of a castle.

 In addition, you could also lose part of their field of vision known as hemianopsia. Instead, you might experience blurring.
In addition, you could also lose part of their field of vision known as hemianopsia. Instead, you might experience blurring.
 Th first of three photos show the view you would normally see. The others are imulations of the loss of vision or blurring that you could see with some types of migraine aura.
Th first of three photos show the view you would normally see. The others are imulations of the loss of vision or blurring that you could see with some types of migraine aura.
Sensory Aura
Sensory aura are the second most common type; they occur in 30–40% of people with auras. You could experience this as a feeling of pins-and-needles begins on one side in the hand and arm. It might even spread to the nose and mouth area on the same side. In addition, you may feel numbness after the tingling has passed with a loss of position sense.
Other Types of Aura
In addition, during the aura phase you might also have speech or language disturbances, vertigo. Finally, auditory hallucinations or delusions have also been described.
Rarely, motor problems occur. This indicates that this is a rare hemiplegic migraine, and weakness often lasts longer than one hour unlike other auras.
No wonder migraine sufferers are treated as if they are crazy sometimes!

Supposedly, in a classic migraine the headache is one side. It is throbbing with moderate to severe intensity.
However, in more than one third of cases, the pain can be on both sides. Sometimes, neck pain is associated with it. In fact, bilateral pain is particularly common in migraines without an aura. Less often, swelling or tenderness of the scalp may occur. You may also have a stiff neck.
A basilar migraine is a migraine with neurological symptoms related to the brain stem. It also refers to neurological symptoms on both sides of the body. Effects include a sense of the world spinning (vertigo), light-headedness, and confusion.
Other Migraine Symptoms
In addition, your the Pain Phase may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting. In addition, you have may sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to smells, fatigue and irritability.
Unfortunately, nausea occurs in almost 90% of people, and vomiting occurs in about one-third.
You may also experience blurred vision, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, frequent urination, pallor, or sweating.
Some of these symptoms are less common as we age.

The migraine postdrome is the constellation of symptoms remaining after the Pain Phase has passed.
You may have a sore feeling in the area where the migraine was.
Also, some people report impaired thinking for a few days after the headache has passed.
However, you may just feel tired or mildly “hung over” and have less intense head pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, depression, mood changes, and weakness.
Some people feel unusually refreshed or euphoric after an attack. There may be psychogical aspects to how different people respond to migraine during Postdrome.
Are You Perpetuating Your Own Headaches?
Structural Variations
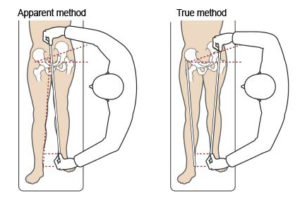

For instance, a difference in either the actual or apparent length our legs is not uncommon. In fact, a difference of 1/4″ can cause myofascial pain.
On the other hand, our legs might be the same length and the two sides of our pelvis might be different sizes. Imbalances caused by myofascial trigger points can pull one side of your hip up while the other falls.
In addition, we can find ourselves out of balance from front to back. For example, this can happen as the result of Morton’s Foot Structure. The slight downward angle created in the foot is like adding a heel to your shoe. Surprisingly, it can pitch your entire body forward. In fact, Morton’s Foot Structure can contribute an inch or more to head forward posture.
Some of us have relatively short upper arms. This means that computers, desks and other furniture is not built for us. Because of this, we might benefit from some changes to our workspace and other environments.
Either way, we are built the way we are and it is ok.6
All of these variations can be accomodated or corrected. Myofascial therapists know how!
How Do You Sit?

Sitting Posture
Obviously, how we sit matters. Of course, there are different kinds of sitting. The way we sit at a desk might be different than how we sit in auto seat or a recliner. However, it should be that different. For instance. in any sitting posture, we want to keep our back fairly straight. Typically, this means no slump in the lumbar spine or upper spine and shoulders. In addition, we want to keep our head and neck reasonably well aligned with our spine. Basically, our hands and arms should be within easy reach of our work - whether it is a keyboard, steering wheel or a desk. Do not lead with your face! Next our legs should be reasonably open at the hip. Unfortunately, the tight flexion of a straight back chair. traditional desk chair or bucket seats shortens our hip flexors and hamstrings. In addition, it overloads our quads and glutes. Finally, it promotes head forward posture overloads the neck and upper spine. Finally, our feet should touch the floor - heels and toe. Often, if you are using a high desk chair, there may be a rail that you can rest your feet on. However, avoid using it. Instead, adjust your chair to a height that allows your feet to touch the floor.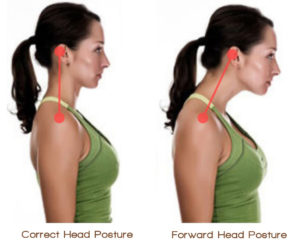
Myofascial and Trigger Point therapists, often recommend simple, gentle exercises to strengthen the deep cervical flexors!
Get Better Sleep, Reduce Chronic Pain

Yes, getting good quality sleep is important!
Sleep is a natural process when we rest and repair ourselves. In fact, a minimum amount of sleep is needed for survival. In addition, we need larger minimum amount of sleep to be at our best.
Ideally, we don’t need to do anything about sleep. We get tired, we go to bed, sleep all night and wake up the next day feel refreshed.
Sadly, sleep often doesn’t go the way we expect. Often, we may be tired when shouldn’t be and unable to fall asleep when we go to bed. Sometimes, we may not sleep through the night. Or, we may sleep enough hours, but not get enough deep sleep. Finally, when we wake up in the morning, for some of us, that is one of the worst times of the day. Now, everything hurts and it takes a significant amount of time to “warm up” and feel better.
First, to get better sleep, we need to do is regulate our schedule.
Set a time to go to bed and get up and stick with it. If you can, the includes weekends.
Also, eating regular meals at consistent times help regulate our systems.
In addition, don’t nap during the day and get adequate sunlight. This helps set your body clock properly.
Avoid habits that interefere with good quality sleep. Make some new good habits. You’ll sleep better!
First, to get better sleep, we need to do is regulate our schedule. Set a time to go to bed and get up and stick with it – even on weekends, if you can. In addition, don’t nap during the day and get adequate sunlight. This helps set your body clock properly.
Avoid habits that interefere with good quality sleep.
Generally, good sleep hygiene is common sense. Most of us already know what do to. But, changing major lifestyle habits is hard. When we realize how far off we’ve gotten from good sleep it can be discouraging.
In that case, consider small steps. Reorganize your bedroom a bit. Focus on reducing just one negative habit and replacing it with one better one.
Rome wasn’t built in a day. One step at a time…
Sleep Posture

Of course, just as when we are awake, some postures are more likely to cause myofacial problems.
Do you sleep on your back, side or stomach? Maybe half-side, half-stomach? But, if on your side, do you curl up? Generally, sleeping flat on your back with little or no pillow is considered natural and ideal.
In fact, this is how infants naturally sleep. However, as older adults, we may find that sleeping on our backs can aggravate low back pain. Also, we are more likely to experience sleep apnea on our back.
So, for for various reasons some of us sleep on our side or stomach. Unfortunately, when we sleep on our stomach our head and neck are turned to one side. Obviously, this causes problems with muscles in head, neck, shoulders and arms.
Sleeping on your stomach is bad. Period.
Often, side sleeping is a great compromise for many people. However, side sleepers need to pay more attention to pillows than people sleeping in other positions. Also, notice the difference for you between ‘half-stomach/half-side” and being purely on your side. True side sleeping means you are laying on your arm OR that you tend to let your shoulder round in. Pillows can help with this.
Most of us sleep with too many pillows, not enough pillows or the wrong kind of pillows. And, this is potent factor is in perpetuating myofascial pain.
Back Sleepers
We recommend a single, very thin pillow under your head. In addition, if you experience low back pain when laying on your back, you may find that bolster under your knees helps. Of course, this could be another ordinary pillow, but a good bolster is round, thick enough and will hold its shape all night.
Side Sleepers
First, we recommend a thick pillow at the head. If you wake up with a hand or arm tucked under your head, that is your body telling you that your pillow is too thin! Side sleeper pillows are either thick and firm OR they have fill that can be positioned as you want it and will mostly keep its shape during sleep.
Next, let’s think about your arms. Naturally, the arm you are sleeping on needs to be accomodated. Try placing a thin pillow under your rib cage. This creates a “slot” for this arm and shoulder. In addition, your upper arm should rest on a thick, firm pillow or bolster. As much as you love your partner, we all need to find a sleeping position that works for us on our own.
Finally, consider your legs. Unfortunately, flexing the hips and/or knees and curling up close to a fetal position is hard on our hip flexors and hamstrings. Try to avoid this. A thick, firm pillow or bolster should be used in between the lower legs. Remember, the idea is to keep your knees and ankles about the same distance apart as your hips.
Avoid foam…
First, we do not recommend foam pillows of any type. Even if you are happy with your foam mattress, we don’t recommend foam pillows. They do not maintain their thickness. In addition, they ‘jiggle’ which is not good for your neck. Of course, it you have any concerns about the foam material itself, you don’t want it near your nose and mouth all night. Besides, there are a variety of other materials that are better for conventional head pillows.
Next, there are a variety of side sleeper pillows in various shapes, including ‘L’ and ‘J’ shaped. For those who go back and forth between back and side sleeping, consider the “Tri-Core” pillow or similar.
Basically, thick pillows and bolsters used to support your limbs need to keep their shape all night. They should be made with dense cotton stuffing or similar.
Feet and Ankles
Sometimes, we need to pay attention to foot and ankle positioning at night. For instance, if we have myofascial issues in the calf, we want to avoid pointing out toes. So, back sleepers probably want to use a bolster of some type to help keep their ankles from drooping at night.
In addition, this means that we might not want heavy covers or sheets tucked in at the foot of the bed. They will weigh down our toes and point our feet and ankles.
Sleep Hygiene

When we are in chronic pain-better sleep is more important than ever. There are many things we commonly eat, drink and imbibe in the evenings that can interfere with your sleep. These are common recommendations for good sleep hygiene.7
Substances
- Caffeine – Some people find that it affects them so strongly that coffee, tea, colas or energy drinks after noon can affect sleep.
- Alcohol – Although alcohol is a depressant, and too much will cause you to pass out, alcohol interferes with your sleep architecture. If you enough, but still feel tired in the morning, consider avoiding alc0hol for 3-4 hours before you go to bed.
- Muscle relaxers, opiates, marijuana (w/THC) – Our advice is similar to alcohol. All are best avoided later in the evening. CBD products may be a different story.
- Liquids – It seems obvious right? We knew this as small children. If you consume significant amounts of liquid before bed, it is much more likely that you will need to get up at night to use the bathroom.
Other Factors
- Blue light – Electronic screens from phones to computers to TVs emit a large amount of blue light that can interfere with sleep. Avoid them for as long as possible before sleep.
- Stress – Getting mentally or emotionally involved in something significant can be stressful. Stress increases cortisol levels. However, cortisol promotes daytime energy and interferes with sleep.
- Exercise – Regular aerobic exercise is good in many ways, including for promoting sleep. However, most of us sleep better if we avoid vigorous exercise in the hours immediately before bed.
If you are already avoiding liquids and getting up at night purely to use the bathroom, this is NOT normal. Men should see a urologist about prostate and/or bladder issues. Both men and women should consider gentle self-care for their pelvic floor. Some pelvic floor issues can be treated externally. Internal therapy for pelvic floor issues is controversial and outside of the scope our practice.
If are able, our bedrooms should be for sleeping only. Our bodies and brains learn what to expect based on what we do and where we do it. If we avoid eating, working, studying and watching TV in the bedroom, it helps to program our system correctly.
We understand biologically that when we go to bed and turn out the lights, it is time for sleep. Instead, if we frequently go to bed, turn out the lights and turn on the TV, we have sent a confusing message to our brain.
Temperature
The temperature of your bedroom under your covers and pajamas is important. If it is already bedtime and we are laying down with the lights out, the next cue that our bodies use is temperature. Cooler temperatures encourage sleep. If you wear pajamas make sure you are not too warm.
Your head, hands and feet are all powerful radiators. If you have trouble falling asleep make sure the room is cool (65-70F), you are not wearing socks, your hands are outside of your covers and your head is uncovered. Maintain adequate humidity in the winter (above 25%).
Avoid drafts, especially on your head and neck. This can activate myofascial trigger points in your neck. Do not make the room too cool. If you are cold at night you are more likely to curl up in a fetal position.
Other Conditions In Your Bedroom
If you have blinds or curtains, use them. Keep your bedroom dark when you are sleeping. Try not to have mirrors positioned that can reflect light on you while you sleep. Avoid flashing lights. Clock radios and other appliances with blue lights can especially troublesome.
Couples
Couples need to work out how to handle schedules that are not aligned. If one of you is having sleeping problems, snoring or otherwise disturbing the other, it may require separate sleeping arrangements for a short while.
Some medications that you are taking may interefere with the amount your sleep. Instead, some can make your sleepy but interfere with the quality of your sleep. Be aware of these effects and discuss them with your doctor.
Medications to promote sleep generally fall into two broad categories.
Medications To Fall Asleep
Melatonin – For example, melatonin is a popular, OTC product that helps us fall asleep. Melatonin is actually a naturally occuring hormone in our body that sends a signal to our brain that it is time for sleep. As we sleep, we use up our melatonin and start making cortisol. When we wake up, our melatonin level should be low and our cortisol level high. This gives us the energy to get through the day. By evening, our cortisol level should be dropping and our melatonin level increasing. The exposure of our eyes to light is one of the ways we make melatonin. If we don’t get enough daylight or our schedule is disrupted by shift work, melatonin 30 minutes before bed might help. We also make less melatonin as we age.
Other sleeping aids, from Sominex to Ambien use different mechanisms to help us fall asleep. Like melatonin, they do not help us STAY asleep.
Medications To Stay Asleep
There are various prescription medications to promote deeper sleep. Consult with your physician for more details.
One of the most commonly prescribed is trazodone. Originally developed as an anti-depressant, small doses of trazodone help some people sleep better. Often, it is prescribed for chronic pain patients. Other types of anti-depressants have also been used to improve sleep.
Pain at night can wake you up. For this reason, muscle relaxants and opiate pain medications may be prescribed before bed. However, these medications may interfere with your sleep architecture. Discuss with your doctor what the best time is for you to take these medications.
Good Sleep Matters!
What Else Contributes To Chronic Headaches?
Do These Things To Feel Better!

- Keep a headache diary - Discover more about what triggers or contributes to your headaches and what treatment is most effective.
- Try relaxation techniques - This can teach you ways to deal with stressful situations. This might help reduce the number of headaches you have.
- Improve your posture - Good posture allows your neck muscles to work properly.
Get Organized
- Improve your work furniture - Consider a standing desk. Make sure your work area is arranged to minimize repetitive head and neck movement.
- Increase aerobic exercise - We go beyond this and encourage healthy movement that my include yoga, dancing, Pilates or other classes.
- Firm up your routines - Don't sleep too much or too little. Set and follow a consistent sleeping schedule. Eat nutritious meals at regular times.
- Drink plenty of fluids - Staying properly hydrated will help, but don't over do it. Alcohol and coffee are dehydrating.
- See The Eye Doctor Regularly - Poorly fitting eyeglasses or improper prescriptions can contribute to headaches. Discuss pros and cons of progressives versus two pairs of glasses, monovision or other approaches.
Coping and support
Living with chronic headaches can be frightening and difficult. The attacks can seem unbearable and make you feel anxious and depressed. Ultimately, they can affect your relationships, your work and the quality of your life. Talking to a counselor or therapist might help you cope with the effects of chronic headaches. And, joining a headache support group can connect you with others. The may have similar experiences and share helpful information.You can do this!
Avoid These Things!

- Stress.
- Smoking.
- Dehydration.
- Excess alcohol.
- Clenching/bruxism.
- Head forward posture.
- Improper (chest) breathing.
- Rebound from caffeine and other medications.